
PODIUM. Journal of Science and Technology in Physical Culture, September-December 2022; 17(3):911-924
Translated from the original in spanish
Original artícle
Setting goals as a motivational technique in athletes
Establecimiento de metas como técnica motivacional en deportistas
Estabelecimento de metas como técnica motivadora para esportistas
Marta Cañizares
Hernández1*![]() https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9504-9779
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9504-9779
Yanet Pérez Surita2![]() https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3220-3000
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3220-3000
1Manuel Fajardo University of Physical Culture and Sports Sciences. Havana Cuba.![]()
2Faculty of Physical Culture. Central University "Marta Abreu" of Las Villas. The Villas, Cuba.![]()
*Corresponding author: marticainder@gmail.com
Received: 2021-11-04
Approved: 2022-06-22
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Goal setting is a fundamental process in sports training and can be used as
a motivational technique in sports to manage the resources of the athlete and the team in order
to enhance cohesion and achieve their aspirations.
Objective: To analyze the relevance of the application of a psychological intervention
program based on the establishment of goals as a motivational technique in the women's team
category 13-14 years of Water Polo of the School of Sports Initiation School Eide " Marcelo Salado", of Villa Clare, Cuba.
Materials and methods: The methodology used includes various research methods and
techniques of a quantitative and qualitative nature. Analysis-synthesis, observation, interview, goal
setting questionnaire, sentence completion technique, management style questionnaire, triangulation
and pre-experiment were used. Descriptive measures of position such as the mean and mode
were calculated. The Wilcoxon signed ranks nonparametric hypothesis test was used to test
whether the changes before and after the intervention were significant.
Results: The measurable data were statistically processed using the SPSS software for
Windows version 17.0. The results demonstrate the influence of the intervention program applied to
improve the team's goal setting.
Conclusions: They value the contribution of the application of the psychological
intervention program, in the establishment of goals in a more objective, clear and understandable way in
the athletes and in the development of the motivational sphere when using the potentialities of
the work of the sports team as a group.
Keywords: Goal setting; Psychological intervention; Motivation; Water polo.
RESUMEN
Introducción: El establecimiento de metas es un proceso fundamental en el
entrenamiento deportivo y puede ser utilizado como una técnica motivacional en el deporte para manejar
los recursos psicológicos del deportista y el equipo en aras de potenciar la cohesión y lograr
sus aspiraciones.
Objetivo: Analizar la pertinencia de la aplicación de un programa de intervención
psicológica sustentado en el establecimiento de metas como técnica motivacional en el equipo
femenino categoría 13-14 años de Polo Acuático de la Escuela de Iniciación Deportiva Escolar Eide
"Marcelo Salado", de Villa Clara, Cuba.
Materiales y métodos: La metodología empleada incluye diversos métodos y técnicas
de investigación de naturaleza cuantitativa y cualitativa. Se utilizaron el análisissíntesis,
observación, entrevista, cuestionario de establecimiento de metas, técnica de completamiento de frases,
el cuestionario de estilo de dirección, la triangulación y el preexperimento. Se calcularon
medidas descriptivas de posición como la media y la moda. Se utilizó la prueba de hipótesis no
paramétrica de rangos señalados de Wilcoxon para comprobar si los cambios antes y después de la
intervención eran significativos.
Resultados: Los datos susceptibles de medición fueron procesados estadísticamente mediante
el software SPSS para Windows versión 17.0 Los resultados demuestran la influencia del
programa de intervención aplicado para el mejoramiento del establecimiento de metas del equipo.
Conclusiones: Valoran la contribución de la aplicación del programa de intervención
psicológica, en el establecimiento de metas de manera más objetivas, claras y comprensibles en las
deportistas y en el desarrollo de la esfera motivacional al utilizar las potencialidades del trabajo del
equipo deportivo como grupo.
Palabras clave: Establecimiento de metas; Intervención psicológica; Motivación; Polo Acuático.
SÍNTESE
Introdução: O estabelecimento de metas é um processo fundamental no treinamento esportivo
e pode ser usado como uma técnica motivacional no esporte para administrar os recursos
psicológicos do atleta e da equipe, a fim de aumentar a coesão e alcançar suas aspirações.
Objetivo: analisar a relevância da aplicação de um programa de intervenção psicológica
baseado no estabelecimento de metas como técnica motivacional na equipe de pólo aquático feminina
de 13-14 anos da Escuela de Iniciación Deportiva Escolar Eide "Marcelo Salado", em Villa Clara, Cuba.
Materiais e métodos: a metodologia empregada inclui vários métodos e técnicas de pesquisa
de natureza quantitativa e qualitativa. Foram utilizadas análise-síntese, observação,
entrevista, questionário de estabelecimento de metas, técnica de preenchimento de frases, questionário
de estilo de gestão, triangulação e pré-experimentação. Foram calculadas medidas descritivas
de posição, tais como média e modo. O teste de hipóteses Wilcoxon não paramétrico assinado
foi usado para testar se as mudanças antes e depois da intervenção eram significativas.
Resultados: Os dados mensuráveis foram processados estatisticamente usando o software
SPSS para Windows versão 17.0. Os resultados demonstram a influência do programa de
intervenção aplicado na melhoria da definição das metas da equipe.
Conclusões: a contribuição da aplicação do programa de intervenção psicológica no
estabelecimento de metas mais objetivas, claras e compreensíveis para as atletas e no desenvolvimento da
esfera motivacional, utilizando o potencial do trabalho da equipe esportiva como um grupo.
Palavras-chave: Definição de objetivos; Intervenção psicológica; Motivação; Polo aquático.
INTRODUCTION
Physical activity in general and sport in particular are forms of human activity relevant to the formation of personality. It is pertinent to highlight the motivational orientation of sports activity, that is, the role of those objectives and motives that drive man to practice sports.
Sport Psychology is a young science and a special branch of Psychology that offers theoretical support to apply scientifically based methodological and intervention programs. For this reason, studies of psychology applied to team sports are promoted, such as Schuster, et al. (2016), Nixdorf, et al. (2016), Alonso, I. (2017), Ekmekçi, et al. (2018), Nascimento et al. (2019), Cañizares et al. (2019) Ramirez, et al. (2020), and psychological intervention programs are applied in sports teams to contribute to performance in training and competition, Tran Thi, (2011), Villalobo, et al. (2020).
Goal setting is a fundamental process in sports training and can be used as a motivational technique in sports to manage the resources of the athlete and the team in order to enhance cohesion and achieve their aspirations. Castle, et al. (2000), Weinberg, R. (2003), García-Más and Gimeno F, (2008), Balaguer, et al. (2015), Eys, et al. (2015), Benson, et al. (2016), Sanchez et al. (2016), Suarez, et al. (2021). Suarez, et al. (2021).
Proper goal setting contributes to the achievement of results in sport.
Locke (1994) reviews 100 studies on goal setting where 90 % showed positive or partially positive effects of goal setting in the direction of athlete preparation.
Most of the research that addresses goal setting has been related to high-performance teams, however, little evidence of its study in sports initiation has been found, Castillo et al. (2000), a stage in which it is necessary to attend to its particularities, given the need to prepare the practitioner for the demands in higher categories. In Cuba, research related to this problem stands out (De la Caridad Suárez-Rodríguez, et al., 2021; Suárez, et al. 2020; Villalobo, et al. 2020; Suarez, et al. (2021).
In the demands of the investigative work practice carried out at the "Marcelo Salado" Sports Initiation School, Sports Initiation School (Eide in Spanish) of Villa Clara, it was possible to work with the coaches of the Water Polo team, category 13-14 female years. These manifested the need to diagnose psychological problems that were affecting the dynamics of the team. For this reason, observations to the team and interviews with the coaches and the athletes were made and the following difficulties could be detected: the absence of a psychologist in the team, lack of knowledge of psychological management in the work of the team as a group, the athletes showed difficulties in the setting goals and did not express commitments or make efforts to achieve the established goals.
In this team, goal setting was done in a very general way. The goals were established by the coaches, without the participation of the athletes. In the latter, there was evidence of poor commitment, lack of will and individualism that had repercussions on interpersonal relationships. In addition, there were few experiences of group work in the team.
For this reason, the objective of the present work consists in analyzing the relevance of the application of a psychological intervention program based on the establishment of goals as a motivational technique in the women's team, category 13-14 years of water polo of the School of Sports Initiation School Eide " Marcelo Salado", from Villa Clara, Cuba.
That is why, the application of a psychological intervention program is justified, which can contribute to the improvement of the goal-setting process in the aforementioned team through the participation of all team members by using the scientific foundations of Sport Psychology, together with the importance conceived by many authors to these factors, López-Salvador et al. (2021) , which implies carrying out studies on the subject in this stage of sports initiation, de Suárez, et al. (2020), Rodríguez, RE (2017), Suárez, et al. (2021).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample
The Water Polo team, category 13-14 years old, female from Eide "Marcelo Salado", Villa Clara, Cuba, participated in the study. All the athletes (18) and the two team coaches participated in the diagnosis, implementation and evaluation of the psychological intervention program. Consent was given, informing the participants of the research and the procedures followed, and they agreed with the ethical standards of the institution.
Methods and instruments
The approach and type of research assumed is essentially quantitative and various methods and techniques of a quantitative and qualitative nature were used. From the theoretical level, the method of analysis-synthesis, induction-deduction, hypothetical-deductive and the systemic approach were used. At the empirical level, scientific observation, the interview, the group goals questionnaire, the sentence completion technique, the management style questionnaire, triangulation and the pedagogical experiment were used. The experiment carried out was of a natural and formative type. Its design is of a pre-experimental type, it begins with an initial control, the intervention and the final control of the studied team.
The observation indicators and indices analyzed are the following:
Actual situation of the team:
Status of interpersonal relationships athlete-athlete, athlete-coach:
The following indicators were defined for goal setting:
The statistical methods used were frequency distributions, contingency tables (double entry) to record the frequency of appearance of the values of two variables simultaneously. Graphical representations were added and descriptive measures of position such as mean and mode were calculated. Wilcoxon `s nonparametric signed rank test of hypothesis was used to test whether the changes before and after the intervention were significant. The data that could be measured were statistically processed using the SPSS software for Windows version 17.0. The stated research methods and techniques are associated with the different phases through which the development of the research went through and are as follows: 1. Diagnosis phase; 2. Preparation phase of the proposal; 3. Implementation phase of the proposal; and 4. Evaluation phase of the proposal.
Procedure
Among the methods used in this second phase are the following: analysis-synthesis, hypothetical-deductive. These theoretical level methods were present throughout the research process, their application made it possible to systematize the conceptions related to the object of study, reveal dimensions and components of the intervention program.
Diagnostic phase: In this phase, the diagnostic techniques were applied: scientific observation, documentary analysis, interview, group goals questionnaire, sentence completion technique, management style questionnaire to know the situation of the team. before setting goals.
Implementation phase of the psychological intervention program
The experiment was brief and was carried out in a short time (around 45 days or a month, before the competition depending on the selected team), with three weekly sessions. An average of 11 intervention sessions were carried out in each of the teams studied with a duration of approximately 1 hour or 85 minutes depending on the development of the sessions.
The application was carried out through the group and individual guidance was provided depending on the situation; A total of 31 sessions were held, twice weekly for four months, each session lasting one hour.
Adequate conditions were guaranteed to carry out the sessions. In general, not only the aspects or behaviors to be changed in each athlete were assessed, but also the influence of the changes to be achieved in the team and the results to be obtained. To make the observations in the competition, there were 13 specialists who were required to comply with certain requirements mentioned in the report. In all of them, feedback techniques were applied at the end of each session where questions were formulated to facilitate feedback on the fulfillment of the proposed goals. Dialogue and participation were encouraged. Individual conversations were held with some athletes and coaches to assess their criteria about the intervention process and to determine compliance with the sessions.
A group of methods and techniques, games, group discussion, reflective participatory techniques, animation and activation techniques, simulations and dialogues were used.
Evaluation phase of the psychological intervention program
For the evaluation of its results, the same methods and techniques of the diagnostic phase and also the experimental method were used. The descriptive statistics processes exposed in the first phase were also used to analyze the behavior of the variable after the program was applied. A pre-experiment with a formative pedagogical nature was carried out. Statistical processing was performed using the Wilcoxon signed rank hypothesis test, which is a before and after test, applicable to ordinal variables.
RESULTS
A detailed analysis of the results obtained by applying each of the methods and techniques described for the first phase was carried out; the results of each method and applied technique are synthesized and finally the results of the triangulation are presented, among which are the following points: As can be seen in table 1, in the interviews with the athletes it is obtained that (Table 1):
Table 1. - Declaration of the athletes about the goals of their team

In the interviews with the coaches, it is obtained that both state that there are problems in the development of some traits of will and motivation to achieve goals in some athletes.
In 90 % of the observations about the real situation of the team, it is observed that there are dissatisfactions in the group and a low level of commitment on the part of the athletes in the establishment of goals is appreciated.
In 90 % of the observations on the status of interpersonal relationships athlete-athlete, athlete-coach, it is appreciated that communication is affected by the difficulties and conflicts that interfere in the relationships between athletes and athletes-coaches and, therefore, thus, the goal-setting process is affected.
From the exploration carried out, it was found that there are difficulties in setting goals in the water polo team, female category 13-14 years of the "Marcelo Salado" School of Sports Initiation, in Villa Clara, Cuba.
As an anticipated response to the formulated problem, the hypothesis following that will lead the pre-experiment:
The application of a psychological intervention program based on the establishment of goals as a motivational technique in the women's team, category 13-14 years of water polo of the School of Sports Initiation (Eide) " Marcelo Salado", Villa Clara, Cuba, will improve team motivation as well as group work.
Next, the behavior of the goal setting indicators is presented before and after the application of the training experiment in the water polo team studied (Table 2).
Table 2. - Behavior of the goal setting indicators before and after application
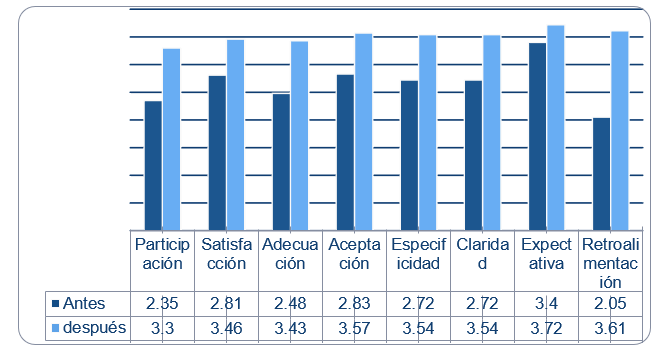
These goals were expressed in the completion of sentences and in the psychological intervention sessions, whose indicators can be seen in Table 1 (Table 3).
Table 3. - Declared goals in the Water Polo team, female category 13-14 years old before and after the intervention program was applied
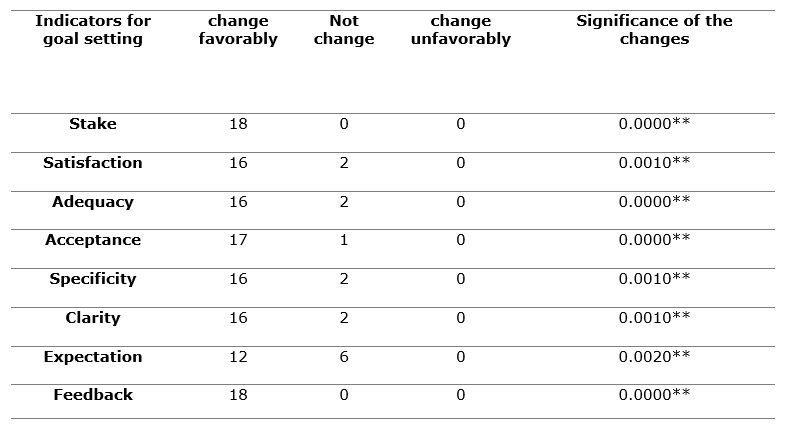
**Very significant changes.
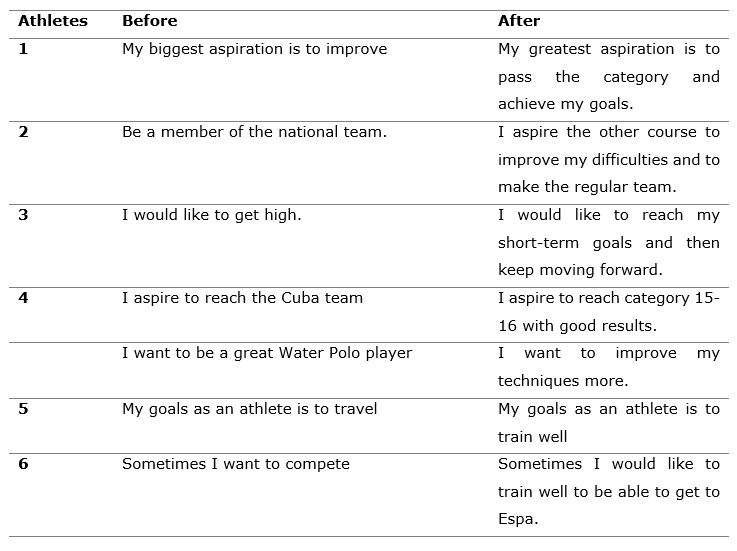
Table 4 shows some examples of individual goals of the athletes before and after the intervention (Tabla 4).
Table 4. - Some examples of individual goals
Some examples of team goals before the intervention:
Medium and long-term goals and in the competition: go to the championship to reach the medal and the participation of all.
Some examples of team goals after the intervention:
Medium and long term and in the competition:
According to the results obtained after applying the pre-experiment in a general sense, the implications of the psychological intervention could be appreciated, derived from the debates, discussions and reflections around the establishment of the goals that were carried out in the team. This was seen in:
This influences the increase in the commitment of the athletes in the achievement of group goals and the satisfaction and participation of the group members for the fulfillment of the goals was evidenced.
The goals are constituted as regulators of the behavior of the athlete and the team, in addition to encouraging responsibility, perseverance, orientation towards an end.
Some achievements of the psychological intervention program evidenced in the interviews with coaches and athletes were:
In 100 % of the observations, it is observed that the coaches perform a systematic feedback on the establishment of goals, which favors better communication in the team.
DISCUSSION
The implementation of the psychological intervention program contributed to a higher motivation in the coaches, to the development of teamwork skills, to an improvement of the goal-setting work in team management.
In the research, the goal-setting theory is systematized according to the psychological peculiarities of adolescence and the use of the potential of group influence on its members at this stage. These results coincide with the Tran Thi (2011), Weinberg, R. (2003) studies, in which the benefits of psychological intervention programs as a motivational technique are appreciated, in addition, in the studies by Suárez, et al. (2020), Rodríguez, RE (2017), Suárez, et al. (2021), coincident results are observed in the sports initiation stage, which corroborates the need to continue applying systems of formative and developing influences that stimulate the development of grouping, of the team mentality in these stages, while they stimulate and motivate to increase sports performance in order to achieve individual and group goals.
The psychological intervention program developed to improve the establishment of goals in the water polo team, female category 13-14 years of the Eide "Marcelo Salado" was based on the stimulation of the participation of the team as a group, promoted discussion, reflection and debates in the sports team around the establishment of goals in training for the competition during and after its application, favorable transformations and significant differences in the indicators studied with respect to the process of establishing goals in the studied team are verified, before and after applying the psychological intervention, which contributes to raising the motivation to meet the team's goals, which corroborates the proposed hypothesis.
REFERENCES
Alonso, I. (2017). La llave del rendimiento. Ebook.
Balaguer, I., Castillo, I., Ródenas, L., Fabra, P., &Duda, J. L. (2015). Los entrenadores como promotores de la cohesión del equipo. Cuadernos de psicología del deporte, 15(1), 233-242. Doi:10.4321/s1578-84232015000100022. https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1578-84232015000100022
Benson, A. J., Šiška, P., Eys, M., Priklerova, S., & Slepièka P. (2016). A prospective multilevel examination of the relationship between cohesion and team performance in elite youth sport. Psychology of Sport and Exercise Journal, 27, 39-46. Doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2016.07.009. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1469029216300899
Cañizares, M; Almanza, C; Paredes, My Cossío, M. (2019). El estudio de la psicología en las actividades físico deportivas: un reto para la escuela actual México: Editorial Chihuahua. http://accion.uccfd.cu/index.php/accion/article/view/55
Castillo,I Balaguer I y Duda J (2000). Las orientaciones de meta y los motivos de práctica deportiva en los jóvenes deportistas valencianos escolarizados. Revista Psicología del Deporte 9. (2). https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=170638
de la Caridad Suárez-Rodríguez, M., Rodríguez-García, R. E., & Cañizares-Hernández, M. (2021). Estudio de las perspectivas de meta en nadadores escolares de La Habana. Study of the goal prospects in scholars swimmers of Havana. Arrancada, 21(38), 130-145. https://revistarrancada.cujae.edu.cu/index.php/arrancada/article/view/359
Ekmekçi, R., y Miçooðullarý, B.O. (2018). Examination and comparison of psychological characteristics of American football players and handball players. Universal J Educ Res, 6(11), 2420-25. doi: 10.13189/ujer.2018.061104. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/227076759.pdf
Eys, M., Evans, M. B., Martin, L. J., et al. (2015). Cohesion and Performance for Female and Male Sport Teams. Sport Psychology, 29(2), 97109.Doi: 10.1123/tsp.2014-0027. https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/tsp/29/2/article-p97.xml
García Más y Gimenos F, (2008) La teoría de orientación de metas y la enseñanza de la Educación Física. Consideraciones prácticas. Revista Latinoamericana de Psicología.40, (3). https://www.apuntesdepsicologia.es/index.php/revista/article/view/256
Locke, E. (1994). Goal setting in sport and exercise: A reaction to Locke comment", Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 6, 16, pp. 212 215. https://journals.humankinetics.com/previewpdf/journals/jsep/15/1/article-p88.xml
López-Salvador, J., Rodríguez-Pérez, M., Paterna, A., & Alcaraz-Ibáñez, M. (2021). Efectos de un programa breve de entrenamiento psicológico y mindfulness sobre el rendimiento psicológico de jugadoras de voleibol sub-16. Psychology, Society & Education, 13(1), 49-60. https://ojs.ual.es/ojs/index.php/psye/article/view/3420
Nascimento Jr, J. R. A.; Silva, A. A.; Granja, C. T. L.; Oliveira, D. V.; Batista, R. P. R.; Fortes, L.S. (2019). Do sporting experiences predict team cohesion in youth athletes? Cuadernos de Psicología del Deporte, 19(3), 102-112. https://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/cpd/v19n3/1578-8423-CPD-19-3-00102.pdf
Nixdorf, I., Frank, R., & Beckmann, J. (2016). Comparison of athletes' proneness to depressive symptoms in individual and team sports: research on psychological mediators in junior elite athletes. Frontiers in psychology. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00893/full
Ramírez-Siqueiros, M. G.; Ceballos-Gurrola, O.; Medina-Rodríguez, R. E.; Reyes-Robles, M.; Bernal-Reyes, F.; Cocca, A. (2020). Factores psicosociales que contribuyen al éxito deportivo de jugadores universitarios de balonmano por posición de juego. Cuadernos de Psicología del Deporte, 20(1), 261-271. https://revistas.um.es/cpd/article/view/356191
Sánchez-Alcaraz M., Bernardino .; Gómez-Mármol, A.; Más Jiménez, M.. (2016) «Estudio de la motivación de logro y orientación motivacional en estudiantes de educación física». Apunts. Educación física y deportes, 2(124), pp. 35-40, https://raco.cat/index.php/ApuntsEFD/article/view/310648
Schuster, S., Sindik, J., y Kavran, U. (2016). Psychological characteristics and traits in male handball playersthe application of multidimensional psychological sports talents scale. Hrvatski športskomedicinski vjesnik, 31(1), 29-38. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/307570226_PSYCHOLOGICAL_CHARACTERISTICS_AND_TRAITS_IN_MALE_HANDBALL_PLAYERS_ -_THE_APPLICATION_OF_MULTIDIMENSIONAL_PSYCHOLOGICAL_SPORTS_TALENTS_SCALE
Suárez, M, Rodríguez, R, E y Cañizares, M (2021) Estudio de las perspectivas de meta en nadadores escolares de La Habana. ARRANCADA. 21 (38), enero-junio, 2021. https://revistarrancada.cujae.edu.cu/index.php/arrancada/article/view/359
Suárez, M, De la Rosa, X y Cañizares, M (2020). Estudio de la motivación de logro en esgrimistas escolares de La Habana. ARRANCADA. 20, (36) enero-junio, 2020. https://revistarrancada.cujae.edu.cu/index.php/arrancada/article/view/307
Villalobo, A, Cruz Nápoles, M y Cañizares, M (2020). Diagnóstico de la cohesión grupal en voleibolistas. Acción, 16, enero-diciembre 2020, E-ISSN: 1812-5808. http://accion.uccfd.cu/index.php/accion/article/view/132
Weinberg, R. (2003). Goal setting in sport and Exercise: results, methodological issues and future. Directions for research. Revista Psicología del Deporte 4 (295). https://www.proquest.com/openview/bb2d324a2072f75424be6be142fbfaae/1?pq -origsite=gscholar&cbl=4385535
Conflicts of interest:
The autors declare that does not exist an interest conflict.
Authors contribution:
Marta Cañizares Hernández: Conception of the idea, search and review of literature, preparation of instruments, application of instruments, collection of information, results of the instruments applied, statistical analysis, preparation of tables, graphs and images, preparation of database, general advice on the topic addressed, drafting of the original (first version), revision and final version of the article, correction of the article, coordinator of the authorship, translation of terms or information obtained.
Yanet Pérez Surita: Literature search and review, preparation of instruments, application of instruments, compilation of the information resulting from the instruments applied, statistical analysis, drafting of the original (first version), correction of the article, review of the application of the bibliographic standard applied.
![]()
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license.
Copyright (c)
2022 Marta Cañizares Hernández, Yanet Pérez Surita