
PODIUM. Journal of Science and Technology in Physical Culture, September-December 2022; 17(3):1243-1254
Translated from the original in spanish
Original artícle
Study of opponents to promote sports intelligence
Estudio de contrarios para fomentar la inteligencia deportiva
Estudo dos oponentes para promover a inteligência esportiva
Antonio Eduardo Becali Garrido1*![]() https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3179-9022
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3179-9022
Tania Ivette Hernández
Echevarría2![]() https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0732-3721
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0732-3721
1National Institute of Sports, Physical Education and Recreation. Inder. Havana Cuba.![]()
2"Manuel Fajardo" University of Physical Culture and Sports Sciences. Havana Cuba.![]()
*Corresponding author:becalijudo@gmail.com
Received:2022-09-04.
Approved:2022-10-19.
ABSTRACT
Introduction: The study of opponents is becoming more and more necessary and in it the use
of information is of vital importance.
Objective: The purpose of the research was to design a tool for the study of opponents in
Cuban high performance.
Materials and methods: Methods such as analytical-synthetic were used; the structural
systemic approach, the documentary review, the SWOT analysis and the observation to determine
the athlete's own characteristics. The proposed tool for the study of opponents allows
accurate decisions to be made in the development of sports preparation and facilitates the development
of strategy and tactics for competitive activity.
Results: It is also possible to socialize the authors' criteria and results obtained from a study
of opponents in the 73kg division of Cuban male judo. The study makes a theoretical approach
on the topics: study of opponents, sports strategy, technique and tactics in sports, as well as
their differences through various indicators. It provides a simple tool for the study of
opponents according to the sport in which it is carried out and emphasizes its flexibility and the need
for generalization to other sports.
Conclusions: The results allow to affirm that the opponents study offers a deep analysis
about their information to cover the needs of the trainer, athletes and the work team.
Keywords: Opponents;Tool; Sports intelligence.
RESUMEN
Introducción: El estudio de contrarios se hace cada vez más necesario y en él cobra
vital importancia el uso de la información.
Objetivo: El propósito de la investigación consistió en diseñar una herramienta para el estudio
de contrarios en el alto rendimiento cubano.
Materiales y métodos: Se emplearon métodos como el analítico-sintético; el enfoque
sistémico estructural, la revisión documental, el análisis DAFO y la observación para determinar
las características propias del atleta. La herramienta propuesta para el estudio de contrarios,
permite tomar decisiones certeras en la elaboración de la preparación deportiva y facilita la elaboración
de la estrategia y la táctica para la actividad competitiva.
Resultados: Se logra además socializar los criterios de los autores y resultados obtenidos a
partir de un estudio de contrarios en la división de 73kg del judo masculino cubano. El estudio realiza
un acercamiento teórico sobre los temas: estudio de contrarios, estrategia deportiva, técnica
y táctica en el deporte, así como sus diferencias mediante varios indicadores. Proporciona
una herramienta sencilla para el estudio de contrarios atendiendo al deporte en que se lleve a cabo
y hace énfasis en su flexibilidad y necesidad de generalización a otros deportes.
Conclusiones: Los resultados posibilitan afirmar que el estudio de contrarios brinda un
profundo análisis de la información de los adversarios para cubrir las necesidades del entrenador,
los deportistas y el equipo de trabajo.
Palabras clave: Contrarios; Herramienta; Inteligencia deportiva.
SÍNTESE
Introdução: O estudo de opostos está se tornando cada vez mais necessário e o uso da informação é de vital importância.
Objetivo: O objetivo da pesquisa consistiu em projetar uma ferramenta para o estudo de opostos em cubanos de alto desempenho.
Materiais e métodos: Métodos como o método analítico-sintético, a abordagem sistêmico-estrutural, revisão documental, análise SWOT e observação foram usados para determinar as características do atleta. A ferramenta proposta para o estudo dos adversários, permite tomar decisões precisas no desenvolvimento da preparação esportiva e facilita o desenvolvimento de estratégias e táticas para a atividade competitiva.
Resultados: Também é possível socializar os critérios dos autores e os resultados obtidos a partir de um estudo dos adversários na divisão de 73 kg do judô cubano masculino. O estudo faz uma abordagem teórica dos temas: contra-estudo, estratégia esportiva, técnica e tática no esporte, assim como suas diferenças por meio de vários indicadores. Ela fornece uma ferramenta simples para o estudo de opostos de acordo com o esporte em que é realizada e enfatiza sua flexibilidade e necessidade de generalização para outros esportes.
Conclusões: Os resultados tornam possível afirmar que o estudo dos adversários permite uma análise profunda das informações dos adversários para cobrir as necessidades do treinador, dos atletas e da equipe de trabalho.
Palavras-chave: Oponentes; Ferramenta; Inteligência esportiva.
INTRODUCTION
The study of opponents is becoming more and more necessary and in it the use of information is of vital importance. Since ancient times, fundamentally in the military field, it was required to study the adversary, this is the case of the classic "The Art of War" by Sun Tzu who emphasizes: "If you know others and you know yourself, neither in a hundred battles you will be in danger; if you don't know others, but you know yourself, you will lose one battle and win another; If you do not know others and yourself, you will be in danger in every battle"
In this ancient Chinese book on military strategy, also considered a treatise on military tactics, the author deals with strategy in a broad way, emphasizing public administration and planning. The text describes theories for battles, but also advocates diplomacy and the cultivation of relationships with other nations as essential to the health of a state. In this sense and in the area of sport, psychologists and scholars of the subject affirm that sports competitions have a certain similarity with war, and other types of contests. This similarity makes it possible to tell experiences used in war and in administration that can provide support to face the opposite and the tactical preparation of athletes and sports teams.
Currently, a relatively new concept has been developed in sports, sports intelligence, this concept does not refer to multiple intelligences, or emotional intelligence, nor is it subject to intelligence quotient, it is a term that represents, among other things, the study of opponents and personalized preparation based on the strengths and weaknesses of the athlete and the opponent.
In the development of a sports activity, especially when it comes to a competition, many factors come into play that can determine success or failure. To such an extent that, according to Santesmases (2010), "in high competition, efficiently achieving elite sports results will depend on the capacity and possibilityy of an athlete or team and their respective coaching groups to manage, analyze and control as much information as possible about the actions of the main actors and factors that affect the competitive performance of their sport". It is not only a physical aspect, but the intellectual and cognitive ones take on an essential nuance in this matter. This is what is known as sports intelligence: the ability to understand what is happening in the sports context: its rules, norms, the interpretation of situations and decision-making accordingly, as well as the adaptation to the capabilities of each athlete.
However, to meet these expectations in sports activity, Dopico and Martínez (2013) state that it is necessary to comply with sports intelligence functions aimed at:
These functions must be carried out in the form of a system, that is, they are related to each other, one gives way to the next, thus they will have interdependence relationships (Synergy) and in the end it returns to the beginning, starting the cycle again so it will comply with the recursion.
The efficient use of information constitutes a vital strategic resource to compete at the highest level and guarantee sporting success. "One of the disciplines of the Management Sciences that facilitates this analysis and control over the relevant information generated by the actions of the main actors and factors that affect the competitive performance of a sport is Sports Intelligence" (Sources et al., 2019). Its importance and usefulness is also also corroborated by authors such as Pérez et al. (2016) and Albarrán (2020).
Athletes, before a competition, have to be able to predict a play, anticipate their opponent or learn to use their abilities for success. It is for this reason that the preparation before a competition can not only be physical, but also involves the acquisition of habits and a lot of previous study.
In sports training, many coaches are vigilant in seeking formulas to achieve high sports results that allow their sport and country to remain in the sports elite. In this area of knowledge, Del Toro and Hernández (2021) argue that both coaching and sports intelligence have become a tool that provides and contributes to the development of strategies aimed at promoting the personal and professional growth of those who strive to achieve proactively success. Specifically, sports intelligence refers to the multilateral preparation of athletes through permanent information assurance for the direction of preparation and development of actions in sports competitions.
In contemporary sport, it is not only important to obtain great results to achieve sports form through the different components of the athlete's preparation, including, the physical and the technical, but also a correct theoretical preparation based on the knowledge and intelligence of the athlete from a search for information that allows collecting, analyzing and executing data of interest for the study of opponents. To achieve this purpose, knowing the dynamics of how the adversary will behave, and predicting, with relative certainty, its strategic and tactical movements is transcendental.
But what is an adversary? This question, in its simplest form of response, is offered by the Dictionary of the Spanish Language RAE, it refers to the opposite or enemy person. In this sense, recognizing an adversary, identifying its potentialities as well as its weak points translates into seizing valuable information to obtain results. The information obtained allows to seize comparative advantages in sport that translate into distinctive skills of the athlete to overcome the opponent. Comparative advantages, according to Hernández (2015) are skills, knowledge, resources and attributes that a sports organization has, and those that its competitors lack or have to a lesser extent. These make it possible to obtain higher yields and the already mentioned distinctive competences. A simple technique to obtain information in relation to the athlete or the sports team is the SWOT analysis, which allows enhancing sports intelligence in its interrelation with competitive strategy, technique and tactics.
This vision is based on the application of studies of opponents in sport from the preparatory period and not only when it is already at the gates of the competition. In contemporary high-performance sport, this must be an inescapable premise and today, given the situation in relation to material and technological resources, it is not fulfilled with due systematicity.
It is important to recognize that a study of opponents carried out in a timely manner and with the quality required by the type of sports discipline is vital for achieving superior results. The objective of the research is to design a tool for the study of opponents in Cuban high performance that can be used by athletes, coaches and technical staff.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In the research, it was used to work with the Cuban male Judo in high performance and the fundamental athlete of the 73kg division of the national team was taken as a sample. The temporality of the study is located during the period prior to the Pan American Games in Lima, Peru, 2019. Theoretical methods were used, such as the analytical-synthetic method, which made possible the analysis of the theory, and the synthesis highlighted by the author on the different criteria on the study of opponents in sport, the structural systemic approach that includes the entire research process and is immersed in the entire procedure carried out during the creation of new knowledge and the documentary review was also used, which allowed to carry out a deep review and detailed training plans and individual plans that were made for the aforementioned multidisciplinary games.
To obtain information in practice, empirical techniques and methods were used, such as the SWOT analysis to establish the weaknesses, threats, strengths and opportunities in the selected division, as well as participant observation to determine the physical characteristics of the athlete and evaluate the development from a technical and tactical point of view.
RESULTS
A simple tool that was applied to Judo in the 73kg division is proposed. This integrates relevant information on judoka, which was derived from a contrary study carried out by the authors of this article. It makes it possible to gather the weaknesses and strengths as well as the opportunities and threats for each athlete both in the technical and tactical fields. It also frames the specific characteristics of their sports performance resulting in information of interest to athletes and coaches. The following table shows this tool (Table 1).
Table 1. - Tool for personalized sports training of judo prctioner
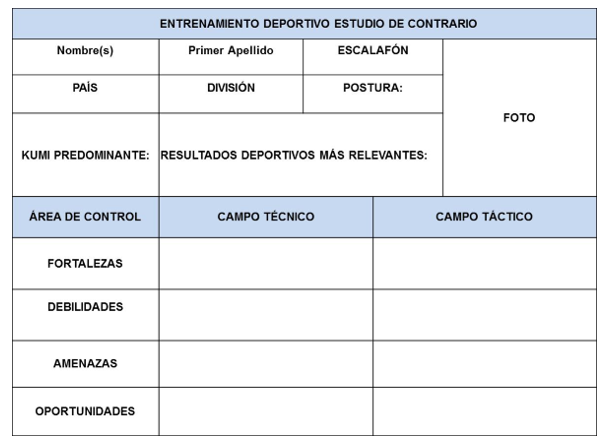
The application of the tool in male Judo, specifically in the 73kg division, was carried out with a view to the Lima 2019 Pan American Games in Peru. The fundamental athletes of this division at this level were determined, resulting in 26 athletes to study. The SWOT analysis was carried out on these judo athletes through the observation of videos of their latest competitions and with the information obtained, the proposed tool was filled as an instrument to carry out the analysis of the opponents. Later, closer to the competition, the pareo that would correspond to the Cuban athlete first figure of the 73kg division was published according to the draw made for the competition. With the pairing, the list of athletes studied was reduced to 15 possible judo athletes to face. Below are four examples of some of the tokens (tool) obtained from the athletes you would have as opponents (Figure 1).
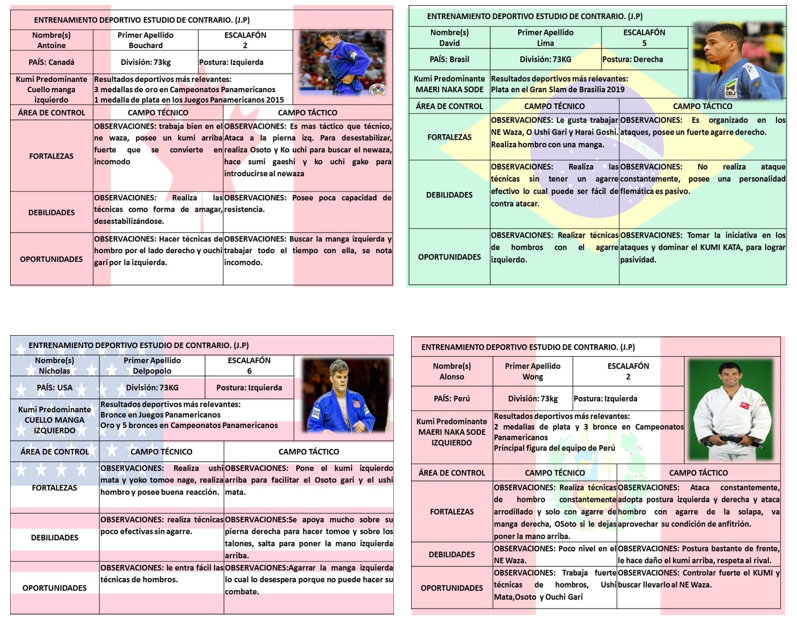
Fig. 1. - Tokens (tool) obtained from the athletes I would have as opponents
The study carried out made it possible for the Cuban athlete and his coach to draw up a competitive strategy that would facilitate the use of the technique depending on the information obtained and with a tactic according to the demands of each opponent. As a result, the Pan American Gold medal was achieved in the division. The investigation carried out constituted the basis for the study with a view to the Tokyo 2020 Games.
This tool is not a rigid instrument as it can be adapted according to the needs of the sport. An example of this can be seen in swimming where, being a sport of times and marks, the study should focus on the times and places obtained by competitive modality. Table 2 shows the modifications of the proposed tool (Table 2).
Table 2.- Modification of the proposed tool for Swimming
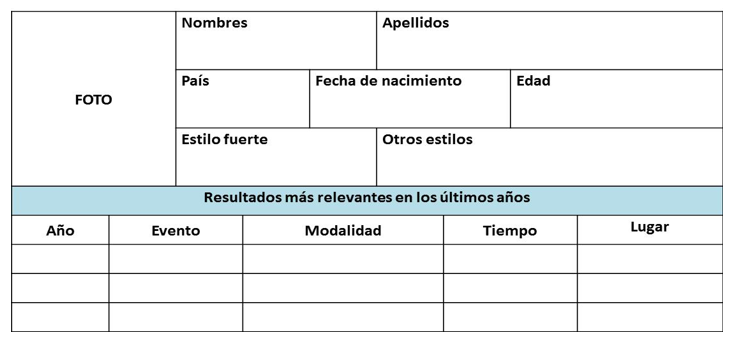
It is important to understand that this research provides a path through a tool to enable the study of opponents. It does not seek, to establish unique prototypes for sports. The tool offers the possibility of self-management of the information by the coach and in this way carry out a job that is complemented by the use of other media such as video. The coach can capture in it, relevant information not only for themselves but also for their athletes because being a simple tool, it allows its widespread use in the different categories. By containing intrinsic aspects of the sport that is practiced, it becomes an instrument to study the opponent. Thus, the knowledge and preparation of the athlete is complemented with the use of sports intelligence based on a search for information that makes it possible to compile, analyze and obtain data of interest for the study of opponents.
DISCUSSION
In sports, important aspects must be considered in a study of the contrary, such as:
In relation to the SWOT analysis as a technique for obtaining information for a study of opponents, the weaknesses, threats, strengths and opportunities are declared. This was obtained from the research carried out in the male Judo in the 73kg division. The study points out that this analysis makes it possible to establish an approach that is as objective as possible of the conditions of the athlete or the team. It is carried out with a team of coaches and specialists who carry out an analysis of information received from the opponent, determining their strengths and weaknesses; followed by a representation of the opportunities and threats that may arise in the competition (Figure 2).
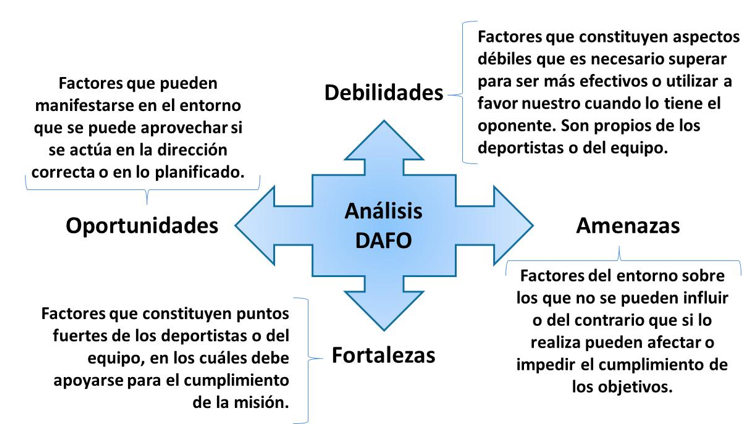
Fig. 2. - Description for a SWOT analysis in sport
The SWOT analysis makes it possible to achieve a characterization of the 73kg athlete under study as well as the opponents he has to face. The result of its application makes it easier to enhance sports intelligence in its interrelation with sports strategy, technique and tactics.
In this regard, Romero and Becali (2014) define for the methodology of sports training, the sports strategy, as well as the technique and tactics in sports.
It takes into account the research of Álvarez (2003) who provides the differences between the terms of strategy, tactics and technique based on indicators (Figure 3).
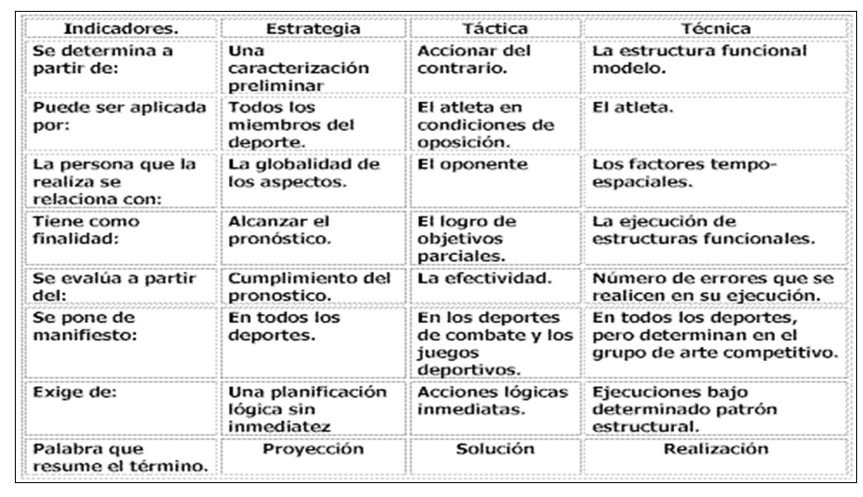
Fig. 3. - Differences between the terms tactics and technique strategy
To enhance sports intelligence Dopico and Martínez (2013) state that it is necessary to comply with a group of principles that work systemically and are:
This last principle supports the appearance of functions, phases, actions and an objective that are not limited only to the study of the opponent. It can be had as much information about the participants in the next competition, use the best and most sophisticated technology for that purpose, even have discussions with the technical group, but the steps to follow and the actions used at the right time. They constitute a chain that allows to evaluate the effectiveness of our planning to obtain achievements through the use of Sports Intelligence.
Therefore, according to these authors, sports intelligence must be aimed at strengthening the competitiveness of the athlete or the team, based on the acquisition and support of the sports form according to the media, in order to have timely and rational responses to situations. that can be presented in competitions. She plays a crucial role when it comes to making decisions at a decisive sporting moment, as well as helping to manage the efforts to achieve a challenge and better understand the objectives to be achieved. You can determine that we achieve the sporting goal that has been set or contribute to its boycott. It is as important as physical preparation.
Sun Tzu stated:
"There are five ways to know the future winner. Those who know when to fight and when not win. Those who know when to use many or few troops. Those who have troops whose upper and lower ranks have the same wish. Those who meet unsuspecting enemies with preparations. Those who have competent generals and not limited by their governments. These five are the ways to meet the future winner."
CONCLUSIONS
The results obtained make it possible to affirm that the study of opponents provides a deep analysis of the information of the adversaries to cover the needs of the coach, the athletes and the work team. The tool designed for the study of opponents, allows accurate decisions to be made in the development of sports preparation and facilitates the development of strategy, technique and tactics for competitive activity. It is well accepted by male Judo athletes and coaches and will be implemented in other divisions. Similarly, its implementation in other sports such as wrestling is being analyzed.
REFERENCES
Albarrán Jardón, E.R. (2020). Inteligencia deportiva: tecnología aplicada al deporte. Pensamiento libre. http://ri.uaemex.mx/bitstream/handle/20.500.11799/110390/PL%2063%20WEB-48%20 -50.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Álvarez, A. (2003). Estrategia, Táctica y Técnica: definiciones,
características y ejemplos de los controvertidos términos. Revista Digital Efdeportes 9(60). https://www.efdeportes.com/efd60/tact.htm
del Toro Reyes, L., & Echeverría, T. I. H. (2021). El Coaching: liberador del potencial para incrementar el máximo desempeño en el deporte. Acción, 17. http://accion.uccfd.cu/index.php/accion/article/view/181
Dopico, H. M. y Martínez, F. (2013). La inteligencia deportiva: una tendencia del deporte contemporáneo. Revista Digital Efdeportes 18(180). https://www.efdeportes.com/efd180/la-inteligencia-deportiva-una-tendencia.htm
Fuentes, A. R., Córdova, B. S., & de Estrada, E. R. D. (2019). La Inteligencia Deportiva en el béisbol cubano. Lecturas: Educación Física y Deportes, 23(250). https://www.efdeportes.com/efdeportes/index.php/EFDeportes/article/view/1192/632
Hernández, T. I. (2015). Las Habilidades directivas para el mejoramiento del desempeño profesional de directivos en las organizaciones deportivas de base. Revista Digital EfDeportes 19(208). https://efdeportes.com/efd200/habilidades-directivas-en-las-organizaciones-deportivas.htm
Pérez, H. M. D., Tellez, I. F., & Farjat, A. B. (2016). Dinámica del trabajo para la inteligencia deportiva en el deporte de alta competencia. Revista Observatorio del Deporte, 2(2). 105-112. https://www.revistaobservatoriodeldeporte.cl/index.php/odep/article/view/95
Romero, R. y Becali, A. E. (2014). Metodología del Entrenamiento Deportivo. La Escuela Cubana. Editorial Deportes. La Habana, Cuba
Santesmases, J. S. (2010). Inteligencia táctica deportiva: entenderla y entrenarla. Barcelona: INDE Publicaciones. https://www.academia.edu/43604920/Inteligencia_tactica_entenderla_y_entrenarla
Tzu, Sun (2008). El Arte de la Guerra. Cuauhtémoc, México: Editorial Porrúa. https://www.elejandria.com/libro/el-arte-de-la-guerra/sun-tzu/847
Conflict of interests:
The authors declare not to have any interest conflicts.
Authors contribution:
The authors have participated in the writing of the work and analysis of the documents.
![]()
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2022
Antonio Eduardo Becali Garrido, Tania Ivette Hernández Echevarrí